What are Genital Warts? Genital warts are swellings that occur on the skin or mucosa as a result of..
More >
Acne Vulgaris (Acne): Diagnosis and Treatment Acne vulgaris is one of the most common skin diseases..
More >
Rosacea (Rosacea): Diagnosis and Treatment Rosacea is a chronic skin disease that typically manifes..
More >
Pruritus (Itching) Diagnosis and Treatment Pruritus (itching) is a common symptom that induces the ..
More >
Diagnosis and Treatment of Herpes Zoster (Shingles) and Herpes Simplex (Cold Sores) Both infections..
More >
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hair and Scalp Diseases Hair and scalp disorders can affect patients' ps..
More >
Diagnosis and Treatment of Alopecia Areata (Spot Baldness) Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease..
More >
Diagnosis and Treatment of Telogen Effluvium (Seasonal Hair Loss) Telogen Effluvium is a type of ha..
More >
Diagnosis and Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Hair Loss) Androgenetic alopecia is ..
More >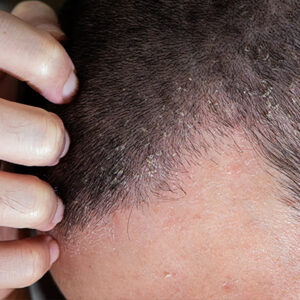
Diagnosis and Treatment of Seborrheic Eczema (Dandruff and Crusting) Seborrheic Dermatitis is a chr..
More >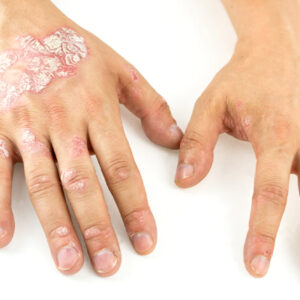
Diagnosis and Treatment of Psoriasis (Psoriatic Disease) Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease ..
More >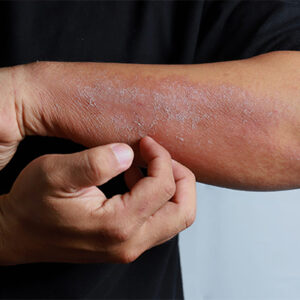
Diagnosis and Treatment of Eczema Diseases Eczema (dermatitis) is a common skin condition character..
More >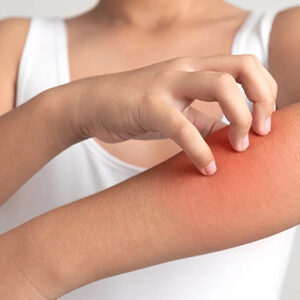
Diagnosis and Treatment of Fungal Diseases Fungal diseases (mycoses) are infections caused by fungi..
More >
Diagnosis and Treatment of Urticaria (Hives) Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a condition cha..
More >
Diagnosis and Treatment of Vitiligo (Leucoderma) Vitiligo is an autoimmune skin disorder characteri..
More >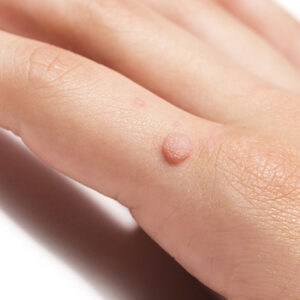
Treatment of Verruca Vulgaris (Warts) and Callus (Corns) Verruca vulgaris and callus are common ski..
More >
Diagnosis and Treatment of Melasma (Facial Pigmentation) Melasma is a common hyperpigmentation cond..
More >
What is Dermatology? Dermatology is the branch of medicine that studies the health, diseases, and c..
More >
 Turkish
Turkish Français
Français